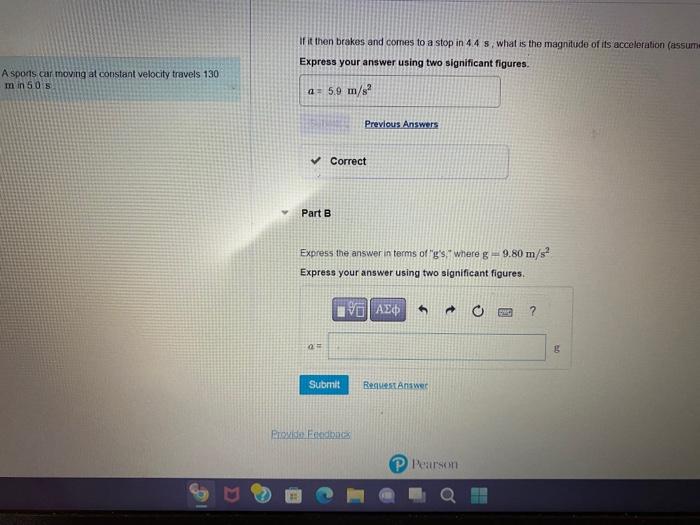
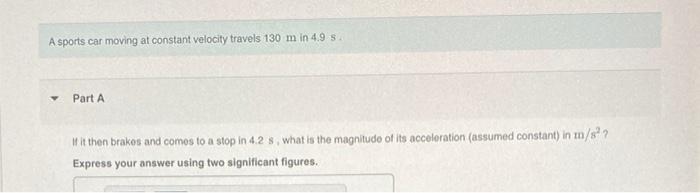
As a sports car moving at constant velocity takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authority and expertise. The discussion that follows promises to unravel the intricate relationship between velocity and sports car performance, providing a comprehensive understanding of this captivating subject.
Delving into the realm of physics, we will explore the concept of constant velocity, distinguishing it from acceleration and showcasing real-world examples. We will then turn our attention to the unique characteristics of sports cars, examining how their design and engineering contribute to their ability to maintain constant velocity.
Constant Velocity

Constant velocity refers to the motion of an object at a constant speed in a specific direction. It implies that the object’s speed and direction remain unchanged over time.
Unlike acceleration, which involves a change in velocity (either speed or direction), constant velocity indicates no acceleration or deceleration.
An example of an object moving at constant velocity is a car traveling on a straight road at a steady speed without changing its direction.
Sports Car in Motion
Sports cars are characterized by their high performance, sleek designs, and enhanced handling capabilities.
The design of a sports car, including its aerodynamic features, suspension system, and engine power, contributes to its ability to maintain constant velocity.
A notable example of a sports car known for its exceptional ability to maintain constant velocity is the Porsche 911 GT3, renowned for its precision handling and stability at high speeds.
Factors Affecting Constant Velocity, A sports car moving at constant velocity
- Wind Resistance:Air resistance increases as speed increases, creating drag that can slow down a sports car.
- Rolling Resistance:Friction between the tires and the road surface creates rolling resistance, which can reduce constant velocity.
- Engine Power:The power output of the engine must be sufficient to overcome resistance forces and maintain constant velocity.
- Driver Input:The driver’s ability to maintain a steady speed and direction through precise steering and throttle control is crucial.
| Factor | Effect on Constant Velocity |
|---|---|
| Wind Resistance | Decreases constant velocity |
| Rolling Resistance | Decreases constant velocity |
| Engine Power | Increases constant velocity |
| Driver Input | Maintains constant velocity |
Applications of Constant Velocity
Constant velocity is essential in sports car racing for several reasons:
- Predictability:Constant velocity allows drivers to anticipate the behavior of their cars, making it easier to navigate corners and maintain control.
- Fuel Efficiency:Maintaining constant velocity reduces fuel consumption compared to fluctuating speeds.
- Safety:Consistent speed helps drivers maintain control, reducing the risk of accidents.
An example of a racing strategy that relies on maintaining constant velocity is the “slipstreaming” technique, where drivers follow closely behind each other to reduce wind resistance and increase speed.
Advanced Concepts
Terminal Velocity:Terminal velocity is the maximum constant velocity an object can achieve when falling through a fluid (e.g., air).
Terminal velocity is reached when the force of gravity pulling the object down is balanced by the force of air resistance pushing the object up.
Calculating Terminal Velocity:The formula for calculating terminal velocity (v t) is:
vt= √(2mg / ρAC d)
where:
- m is the mass of the object
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
- ρ is the density of the fluid
- A is the cross-sectional area of the object
- C dis the drag coefficient of the object
FAQ Overview: A Sports Car Moving At Constant Velocity
What is constant velocity?
Constant velocity refers to the motion of an object at a constant speed in a straight line, without any change in its direction or magnitude.
How does a sports car’s design affect its ability to maintain constant velocity?
The design of a sports car, including its aerodynamics, suspension, and powertrain, is optimized to minimize resistance and maintain stability, enabling it to achieve and sustain constant velocity.
What are some applications of constant velocity in sports car racing?
Constant velocity is crucial in sports car racing for maintaining optimal tire grip, maximizing fuel efficiency, and achieving consistent lap times.