Enzymes, the intricate molecular machines that orchestrate biochemical reactions within living organisms, have captivated the scientific community for centuries. Their remarkable properties and diverse applications have fueled countless studies, yet misconceptions persist. This exploration delves into which of the following statements regarding enzymes is false, separating truth from fiction and shedding light on the fundamental principles that govern these biological catalysts.
Enzymes, unlike their non-enzymatic counterparts, possess unique characteristics that enable them to perform their catalytic functions with unmatched efficiency and specificity. They facilitate reactions without being consumed, a testament to their remarkable ability to accelerate chemical transformations while remaining intact.
Moreover, their specificity, ranging from substrate to reaction and stereochemical, ensures precise and selective interactions with target molecules, contributing to the intricate choreography of metabolic pathways.
Enzyme Characteristics: Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Enzymes Is False
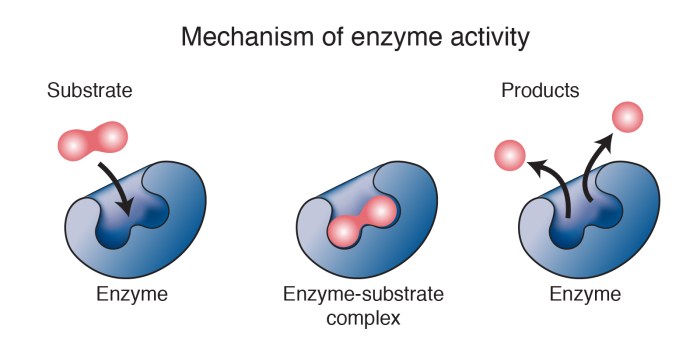
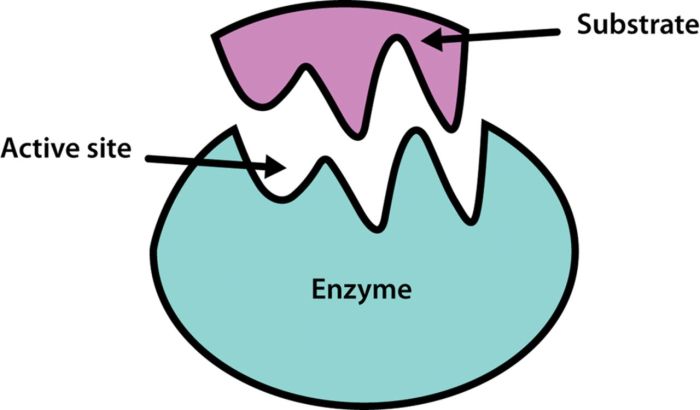
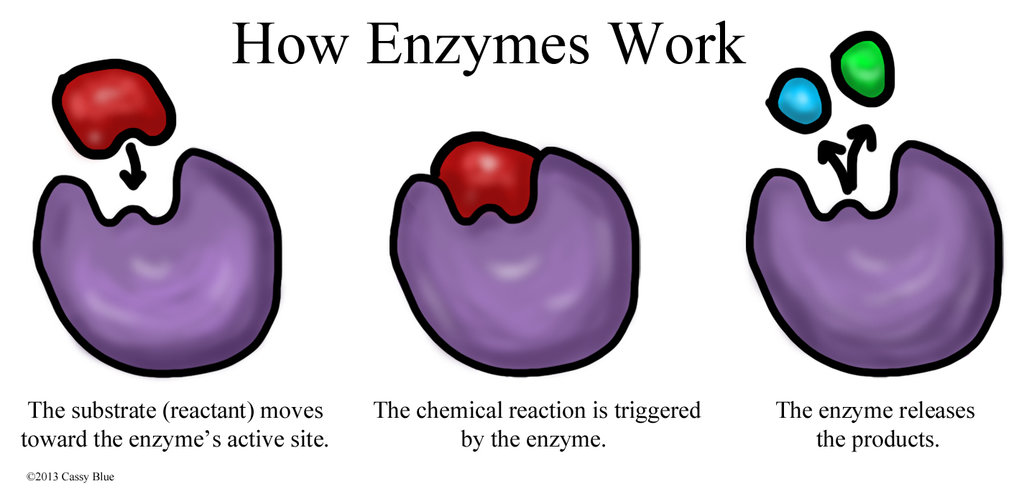
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions. They are highly specific and can dramatically increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed. The following table compares the characteristics of enzymes with non-enzymes:| Feature | Enzymes | Non-enzymes ||—|—|—|| Structure | Proteins with a specific 3D structure | Can be proteins or non-proteins || Function | Catalyze specific chemical reactions | Do not catalyze reactions || Specificity | Highly specific for their substrates | Can be non-specific || Efficiency | Can increase reaction rates by millions of times | Increase reaction rates by a few times || Consumption | Not consumed in the reaction | Consumed in the reaction |Enzymes possess unique properties that distinguish them from other proteins.
They have a specific 3D structure that forms an active site, which is a region that binds to the substrate and facilitates the reaction. Enzymes also exhibit high specificity for their substrates, meaning they only catalyze a specific reaction or set of reactions.
This specificity is essential for regulating metabolic pathways and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Enzyme Specificity
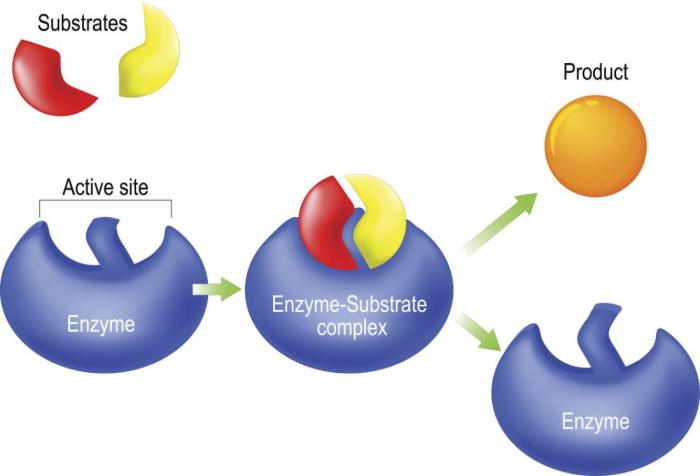
Enzyme specificity refers to the ability of enzymes to catalyze specific reactions or bind to specific substrates. There are three main types of enzyme specificity:Substrate Specificity: Enzymes are highly specific for their substrates, meaning they only bind to and catalyze reactions involving a particular substrate or a small group of related substrates.Reaction
Specificity: Enzymes are also specific for the reactions they catalyze. They can only catalyze a particular reaction or a small group of related reactions.Stereochemical Specificity: Enzymes can distinguish between different stereoisomers of a substrate. They can catalyze reactions involving only one specific stereoisomer or produce only one specific stereoisomer of a product.Enzyme
specificity is crucial for the efficiency of metabolic pathways. It ensures that reactions occur in the correct order and that the correct products are formed.
Enzyme Inhibition
Enzyme inhibition is the process by which the activity of an enzyme is decreased or stopped. There are three main types of enzyme inhibition:Competitive Inhibition: In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme, competing with the substrate for binding.
This type of inhibition can be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate.Non-competitive Inhibition: In non-competitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to a site on the enzyme other than the active site. This type of inhibition cannot be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate.Uncompetitive
Inhibition: In uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to a complex formed between the enzyme and the substrate. This type of inhibition can only occur when the enzyme-substrate complex is formed.Enzyme inhibitors are used in medicine and industry to treat diseases and regulate biochemical processes.
For example, statins are a class of drugs that inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in cholesterol synthesis.
Q&A
Is it true that enzymes are always proteins?
No, not all enzymes are proteins. Some enzymes, known as ribozymes, are composed of RNA molecules and possess catalytic activity.
Can enzymes catalyze reactions in both directions?
While enzymes typically facilitate reactions in one specific direction, some enzymes, known as bidirectional enzymes, can catalyze reactions in both forward and reverse directions.
Do enzymes lose their activity once they bind to their substrates?
No, enzymes do not lose their activity upon binding to their substrates. In fact, substrate binding is essential for enzyme catalysis.