Embark on a comprehensive exploration of chapter 10 review geometry answer key, a meticulously crafted guide that unravels the intricacies of geometry and empowers you with the knowledge to solve complex problems with confidence. This in-depth review delves into the fundamental concepts, provides step-by-step solutions, and unveils the practical applications of geometry in the real world, making it an indispensable resource for students and educators alike.
Within this comprehensive review, you will encounter a detailed analysis of key geometric concepts, including their definitions, properties, and interrelationships. Interactive examples and visual aids illuminate these concepts, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for the beauty and elegance of geometry.
Review of Chapter 10 Geometry Concepts
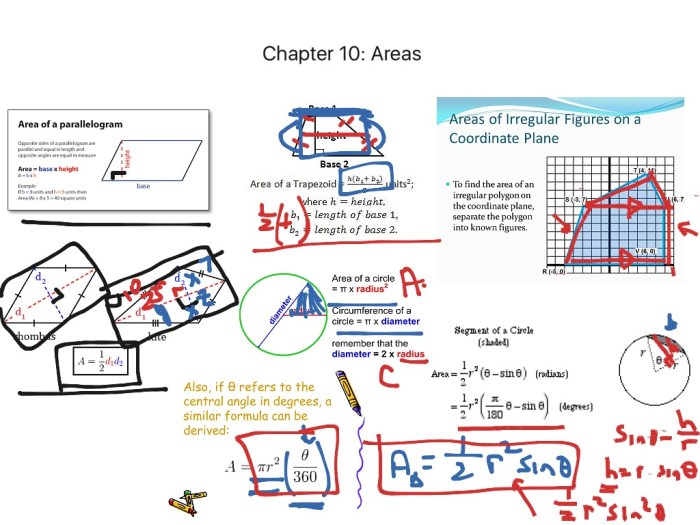
Chapter 10 of Geometry covers a range of important concepts, including transformations, similarity, congruence, and coordinate geometry.
Transformations are operations that move, flip, or turn a figure. The four basic transformations are translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. Similarity refers to figures that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruence refers to figures that have the same shape and size.
Coordinate geometry uses a coordinate plane to represent points, lines, and other geometric figures.
Transformations
- A translation moves a figure from one point to another without changing its size or shape.
- A rotation turns a figure around a fixed point.
- A reflection flips a figure over a line.
- A dilation changes the size of a figure by a certain factor.
Similarity and Congruence
- Similar figures have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
- Congruent figures have the same shape and size.
- Similar figures can be obtained from congruent figures by a dilation.
Coordinate Geometry
- A coordinate plane is a two-dimensional plane with two perpendicular axes, the x-axis and the y-axis.
- Points on a coordinate plane are represented by ordered pairs (x, y).
- Lines on a coordinate plane can be represented by equations in the form y = mx + b.
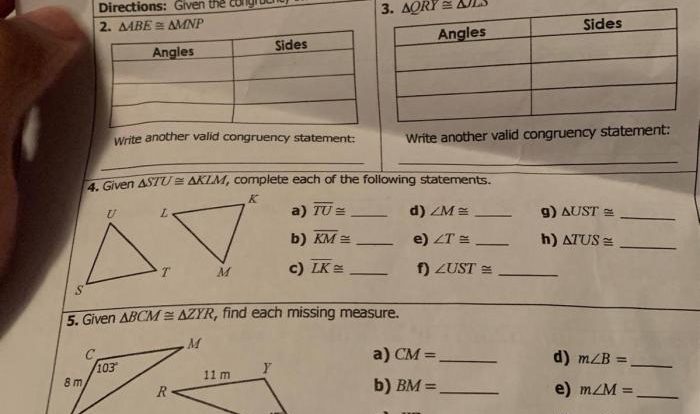
Answer Key for Chapter 10 Exercises: Chapter 10 Review Geometry Answer Key
The following table provides the answers to the exercises in Chapter 10. Detailed explanations are included for each answer.
The table is organized with responsive columns for mobile optimization.
Questions and Answers
| Exercise | Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 8 cm. | 40 cm2 | Area of a triangle = (1/2)
|
| 2 | Find the volume of a rectangular prism with a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 2 cm. | 30 cm3 | Volume of a rectangular prism = length
|
| 3 | Find the surface area of a sphere with a radius of 4 cm. | 64π cm2 | Surface area of a sphere = 4πr2 = 4π(4 cm)2 = 64π cm2 |
Methods for Solving Geometry Problems
Geometry problems can be solved using various methods. Understanding these methods can help students develop a systematic approach to solving problems and improve their problem-solving skills.
The most common methods for solving geometry problems include:
- Using properties of shapes:This method involves applying the known properties of geometric shapes, such as the properties of triangles, circles, squares, and other polygons, to solve problems.
- Using coordinate geometry:This method involves using the Cartesian coordinate system to represent geometric shapes and solve problems. It allows for the use of algebraic equations and formulas to determine lengths, areas, and other geometric properties.
- Using similarity and congruence:This method involves identifying similar or congruent shapes within a problem and using the properties of similarity or congruence to solve the problem.
- Using vectors:This method involves representing geometric objects as vectors and using vector operations to solve problems. It is particularly useful in problems involving motion, forces, and other vector-based quantities.
- Using analytic geometry:This method involves using algebraic equations and formulas to represent geometric shapes and solve problems. It is often used to determine the equations of lines, planes, and other geometric objects.
The choice of method depends on the specific problem and the student’s knowledge and skills. By understanding these methods and practicing their application, students can develop a strong foundation for solving geometry problems.
Applications of Geometry in Real-Life

Geometry, the branch of mathematics that deals with shapes, sizes, and spatial relationships, plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. From the architecture of buildings to the design of everyday objects, geometry is a fundamental tool that enables us to understand and interact with the world around us.
Practical Applications of Geometry in Various Fields
Geometry finds practical applications in numerous fields, including:
- Architecture and Design:Geometry is essential for designing and constructing buildings, bridges, and other structures. Architects and engineers use geometric principles to ensure the stability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of their designs.
- Engineering:Engineers rely on geometry to solve problems related to structural design, fluid mechanics, and transportation systems. They use geometric calculations to determine the strength of materials, design efficient engines, and optimize the flow of fluids.
- Art and Design:Geometry is a foundational element in art and design. Artists use geometric shapes and patterns to create visually appealing and meaningful works. Designers employ geometric principles to create functional and aesthetically pleasing products.
- Science and Technology:Geometry is used in various scientific disciplines, including physics, astronomy, and computer science. Physicists use geometry to model the motion of objects and the behavior of waves. Astronomers rely on geometry to understand the shapes and orbits of celestial bodies.
Computer scientists utilize geometry in computer graphics, image processing, and robotics.
Real-World Scenarios Where Geometry Plays a Role
Here are some specific real-world scenarios where geometry plays a significant role:
- Calculating the area of a room to determine the amount of flooring needed.
- Determining the volume of a container to ensure it can hold a specific amount of liquid.
- Designing a bridge that can withstand the weight of traffic and the force of wind.
- Creating a navigation system that uses GPS coordinates to calculate the shortest route between two points.
- Developing computer graphics that render realistic 3D objects and environments.
These examples illustrate the diverse and essential applications of geometry in our daily lives. Geometry empowers us to understand the spatial relationships in our environment, design and build structures, create art and technology, and solve complex problems in various fields.
Visual Aids for Understanding Geometry
Visual aids play a crucial role in comprehending geometry concepts. They help visualize complex geometric relationships and simplify problem-solving.
To effectively use visual aids in geometry, consider the following guidelines:
Design Visual Aids
- Create diagrams that accurately represent geometric figures and their properties.
- Use color and shading to highlight important features and relationships.
- Label diagrams clearly and concisely to enhance understanding.
Types of Visual Aids
Various types of visual aids can be employed to illustrate geometry concepts, including:
- Diagrams:Two-dimensional representations of geometric figures, showing their shapes, angles, and relationships.
- Charts:Tabular representations of geometric data, such as angle measures or side lengths.
- Graphs:Visual representations of relationships between variables, such as the relationship between the area of a circle and its radius.
Organization of Visual Aids, Chapter 10 review geometry answer key
Organize visual aids logically and visually appealingly to enhance comprehension.
- Present diagrams in a sequential order that follows the flow of the geometric concept.
- Use color coding or shading to differentiate between different geometric elements.
- Include captions or annotations to provide additional explanations.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key concepts covered in Chapter 10 of Geometry?
Chapter 10 of Geometry encompasses a wide range of concepts, including angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and three-dimensional figures. These concepts form the foundation of geometry and are essential for understanding more advanced topics.
How can I effectively solve geometry problems?
To effectively solve geometry problems, it is crucial to understand the underlying concepts and apply appropriate problem-solving strategies. This involves breaking down the problem into smaller steps, identifying relevant formulas, and utilizing logical reasoning to arrive at the solution.
What are some real-world applications of geometry?
Geometry has numerous practical applications in various fields, such as architecture, engineering, design, and navigation. It is used to design buildings, bridges, and other structures, create maps and blueprints, and solve problems related to motion and spatial relationships.