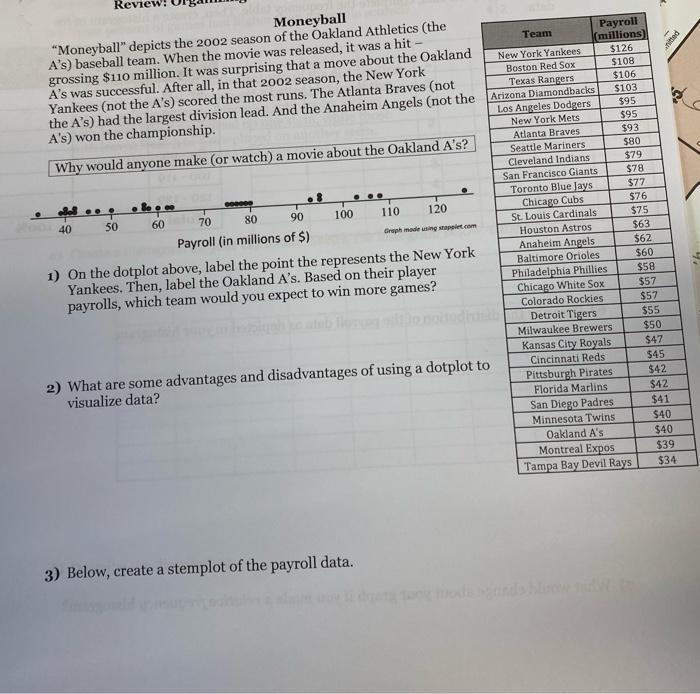
The stemplot shows the number of home runs, offering a captivating glimpse into the world of baseball statistics. This visual representation provides a powerful tool for understanding the distribution of home runs, revealing patterns and insights that would otherwise remain hidden.
By delving into the structure and interpretation of the stemplot, we embark on a journey to uncover the secrets it holds. From deciphering the relationship between stems and leaves to constructing frequency distributions, we unravel the complexities of home run data, unlocking its potential for informed analysis.
Overview of the Stemplot

A stemplot is a graphical representation of a set of data that displays the distribution of data values in a way that makes it easy to see the shape, center, and spread of the data.
A stemplot consists of two parts: the stem and the leaf. The stem is the leftmost digit of the data value, and the leaf is the remaining digits.
Data Interpretation
To interpret a stemplot, first, look at the stems. The stems represent the tens or hundreds place of the data values. For example, a stem of 1 represents data values in the tens place, a stem of 2 represents data values in the hundreds place, and so on.
Next, look at the leaves. The leaves represent the ones place of the data values. For example, a leaf of 3 represents a data value of 13, a leaf of 7 represents a data value of 17, and so on.
Frequency Distribution
A frequency distribution is a table that shows the number of times each data value occurs in a data set.
To create a frequency distribution from a stemplot, first, count the number of times each stem appears. Then, write the stems in a column. Next, count the number of times each leaf appears for each stem. Then, write the leaves in a row next to the corresponding stem.
Statistical Measures
Several statistical measures can be derived from a stemplot, including the mean, median, and mode.
The mean is the average of the data values. To calculate the mean from a stemplot, multiply each stem by the number of times it appears and then add up the products. Then, divide the sum by the total number of data values.
The median is the middle value in a data set. To calculate the median from a stemplot, first, find the middle stem. Then, count the number of leaves for the middle stem. If the number of leaves is even, the median is the average of the two middle leaves.
If the number of leaves is odd, the median is the middle leaf.
The mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a data set. To find the mode from a stemplot, look for the stem with the most leaves.
Visual Representation, The stemplot shows the number of home runs
A stemplot can be presented in a visually appealing way using an HTML table.
To create an HTML table for a stemplot, first, create a table with two columns. The first column should be labeled “Stem” and the second column should be labeled “Leaf”.
Next, fill in the table with the stems and leaves from the stemplot. You can use the (non-breaking space) character to separate the stem from the leaf.
Essential FAQs: The Stemplot Shows The Number Of Home Runs
What is the purpose of a stemplot?
A stemplot is a visual representation of data that allows for easy identification of patterns and outliers. It is particularly useful for displaying distributions of numerical data, such as the number of home runs hit by a baseball player.
How do I interpret a stemplot?
A stemplot consists of two parts: the stem and the leaf. The stem represents the tens digit of the data value, while the leaf represents the ones digit. To interpret a stemplot, simply read the stems and leaves together to obtain the complete data values.
What are the advantages of using a stemplot?
Stemplots offer several advantages over other data visualization methods. They are easy to construct, provide a clear representation of the data distribution, and allow for quick identification of outliers and patterns.