Delve into the realm of AP Macroeconomics Unit 2 FRQ Answers, where economic principles converge to illuminate the complexities of our financial world. This guide unveils the intricacies of macroeconomic measurement, economic growth, inflation, unemployment, fiscal policy, and monetary policy, empowering you with a profound understanding of these fundamental concepts.
Unveiling the nuances of GDP, GNP, and NNP, we embark on a journey to explore their distinctions and limitations. The factors that drive economic growth are meticulously examined, revealing the key characteristics of its various stages. Inflation’s multifaceted nature is dissected, delving into its causes and consequences, while the role of monetary policy in its control is illuminated.
Macroeconomic Measurement

Macroeconomic measurement involves quantifying the overall performance of an economy. Three key measures used are Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Gross National Product (GNP), and Net National Product (NNP).
Concepts of GDP, GNP, and NNP
- GDP: The total value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders during a specific period (usually a quarter or a year).
- GNP: The total value of all final goods and services produced by a country’s residents, regardless of their location, during a specific period.
- NNP: The total value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders during a specific period, minus depreciation.
Comparison and Contrast of GDP, GNP, and NNP
| Measure | Definition | Includes | Excludes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | Value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders | Domestic production | Foreign production by domestic residents |
| GNP | Value of goods and services produced by a country’s residents | Domestic and foreign production by domestic residents | Foreign production by non-residents |
| NNP | Value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders, minus depreciation | Domestic production | Foreign production by domestic residents, depreciation |
Limitations of Using GDP as a Measure of Economic Well-being
While GDP is a widely used measure of economic performance, it has limitations:
- Ignores non-market activities: GDP only includes goods and services that are bought and sold in the market, excluding unpaid work, such as housework or volunteerism.
- Does not measure income distribution: GDP does not indicate how income is distributed among the population, which can affect overall well-being.
- Environmental externalities: GDP does not account for negative environmental impacts associated with economic activities.
Economic Growth: Ap Macroeconomics Unit 2 Frq Answers
Economic growth refers to the sustained increase in the production of goods and services in an economy over time. It is a complex process influenced by various factors, including capital accumulation, technological advancements, and human capital development. Economic growth is essential for improving living standards, reducing poverty, and fostering sustainable development.
Factors Contributing to Economic Growth
- Capital Accumulation:Investment in physical capital, such as machinery, infrastructure, and buildings, increases the productive capacity of an economy.
- Technological Advancements:Innovations and technological breakthroughs lead to increased productivity, efficiency, and new products or services.
- Human Capital Development:Education, training, and healthcare improve the skills and knowledge of the workforce, enhancing their productivity and adaptability.
- Natural Resources:Abundance of natural resources, such as minerals, energy, and fertile land, can provide a foundation for economic growth.
- Government Policies:Stable macroeconomic policies, such as low inflation, sound fiscal management, and supportive regulatory frameworks, foster an environment conducive to investment and growth.
Stages of Economic Growth
| Stage | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Pre-Industrial | Agriculture-based economy, limited technology, low productivity |
| Industrialization | Rapid technological advancements, growth of manufacturing and urbanization |
| Post-Industrial | Service-oriented economy, emphasis on knowledge and innovation |
| Knowledge Economy | Intensive use of information and communication technologies, highly skilled workforce |
Challenges and Opportunities of Economic Growth
Economic growth brings both challenges and opportunities:
- Challenges:Income inequality, environmental degradation, and social tensions can accompany rapid growth.
- Opportunities:Increased living standards, job creation, and improved healthcare and education.
Inflation
Inflation refers to a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time. It is measured as the percentage change in the price level from one period to another, typically a year.
There are different types of inflation, classified based on the severity and underlying causes:
- Creeping Inflation:Mild inflation, typically below 3% annually, where prices rise gradually and steadily.
- Walking Inflation:Moderate inflation, ranging from 3% to 10% annually, where prices rise at a noticeable but not alarming rate.
- Galloping Inflation:Rapid inflation, exceeding 10% annually, where prices increase quickly and significantly.
- Hyperinflation:Extreme inflation, with prices rising at an uncontrolled rate, often exceeding 50% per month.
Causes of Inflation
Inflation can be caused by various factors, including:
| Demand-Pull Inflation | Cost-Push Inflation |
|---|---|
|
|
Consequences of Inflation
Inflation can have significant consequences for an economy:
| Positive Consequences | Negative Consequences |
|---|---|
|
|
Role of Monetary Policy in Controlling Inflation
Central banks use monetary policy to control inflation. The primary tools of monetary policy are:
- Open Market Operations:Buying and selling government securities to influence the money supply.
- Reserve Requirements:Setting the minimum amount of reserves banks must hold, affecting the money supply.
- Discount Rate:The interest rate at which banks borrow from the central bank, influencing the cost of borrowing for banks and their customers.
By adjusting these tools, central banks can influence the money supply, interest rates, and overall economic activity, ultimately affecting inflation.
Unemployment
Unemployment is a major economic issue that can have significant consequences for individuals, families, and the economy as a whole. It occurs when people who are willing and able to work cannot find jobs.
Types of Unemployment
There are several different types of unemployment, including:
- Frictional unemploymentoccurs when workers are temporarily unemployed while searching for new jobs or transitioning between jobs.
- Structural unemploymentoccurs when workers lack the skills or qualifications required for available jobs.
- Cyclical unemploymentoccurs during economic downturns when businesses lay off workers due to decreased demand for goods and services.
- Seasonal unemploymentoccurs in industries that experience fluctuations in demand throughout the year, such as tourism or agriculture.
Natural Rate of Unemployment vs. Cyclical Rate of Unemployment
The natural rate of unemployment is the level of unemployment that exists even when the economy is at full employment. It includes frictional and structural unemployment, which are considered unavoidable in a dynamic economy.
The cyclical rate of unemployment is the additional unemployment that occurs during economic downturns. It is caused by a decrease in aggregate demand, which leads to businesses laying off workers.
| Characteristic | Natural Rate of Unemployment | Cyclical Rate of Unemployment |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Frictional and structural unemployment | Decrease in aggregate demand |
| Duration | Persistent | Temporary |
| Policy Response | Structural policies (e.g., job training) | Demand-side policies (e.g., fiscal stimulus) |
Government Policies to Reduce Unemployment
Governments can implement various policies to reduce unemployment, including:
- Fiscal policy, such as tax cuts or increased government spending, can stimulate aggregate demand and create jobs.
- Monetary policy, such as lowering interest rates, can make it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest in new projects, leading to job creation.
- Structural policies, such as job training programs or education reforms, can help workers acquire the skills and qualifications needed for available jobs.
- Wage subsidiescan encourage businesses to hire new workers or retain existing ones.
- Public works projectscan create temporary jobs and stimulate the economy.
Fiscal Policy

Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. It is a powerful tool that can be used to stimulate economic growth, reduce unemployment, and control inflation.
Tools of Fiscal Policy
The main tools of fiscal policy are government spending and taxation.
Government spending
Government spending can be used to increase aggregate demand, which is the total demand for goods and services in an economy. This can lead to increased production, employment, and economic growth.
Taxation
Taxation can be used to reduce aggregate demand. This can lead to decreased production, employment, and economic growth.
Expansionary and Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy can be either expansionary or contractionary.
- Expansionary fiscal policyis used to stimulate economic growth. This is done by increasing government spending or reducing taxes.
- Contractionary fiscal policyis used to reduce inflation or slow down economic growth. This is done by decreasing government spending or increasing taxes.
The following table summarizes the effects of expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy:| Fiscal Policy | Government Spending | Taxes | Aggregate Demand | Production | Employment | Inflation ||—|—|—|—|—|—|—|| Expansionary | Increase | Decrease | Increase | Increase | Increase | Decrease || Contractionary | Decrease | Increase | Decrease | Decrease | Decrease | Increase |
Challenges of Implementing Fiscal Policy Effectively
There are a number of challenges to implementing fiscal policy effectively.
Time lags
Fiscal policy can take time to have an effect on the economy. This is because it can take time for the government to implement new spending programs or tax changes.
Political constraints
Fiscal policy can be difficult to implement due to political constraints. For example, politicians may be reluctant to raise taxes or cut spending, even if it is necessary to do so for the economy.
Unintended consequences
Fiscal policy can have unintended consequences. For example, expansionary fiscal policy can lead to inflation if it is not implemented carefully.Despite these challenges, fiscal policy remains a powerful tool that can be used to influence the economy. When used effectively, fiscal policy can help to promote economic growth, reduce unemployment, and control inflation.
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank to control the money supply and interest rates within an economy. It is a key tool used to influence economic activity, inflation, and unemployment.
Tools of Monetary Policy
Central banks use various tools to implement monetary policy, including:
- Open Market Operations:Buying and selling government securities to inject or withdraw money from the financial system.
- Reserve Requirements:Setting the minimum amount of reserves that banks must hold, which affects the amount of money they can lend out.
- Discount Rate:The interest rate charged to banks when they borrow from the central bank, which influences the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers.
Effects of Monetary Policy, Ap macroeconomics unit 2 frq answers
The effects of monetary policy can be summarized as follows:
| Expansionary Monetary Policy | Contractionary Monetary Policy |
|---|---|
|
|
Challenges of Monetary Policy
Implementing monetary policy effectively can be challenging due to several factors, including:
- Time Lags:The effects of monetary policy can take time to manifest, making it difficult to predict the appropriate level of intervention.
- Unintended Consequences:Monetary policy can have unintended consequences, such as asset bubbles or financial instability.
- Global Economic Factors:External factors, such as global economic conditions or exchange rates, can complicate the implementation of domestic monetary policy.
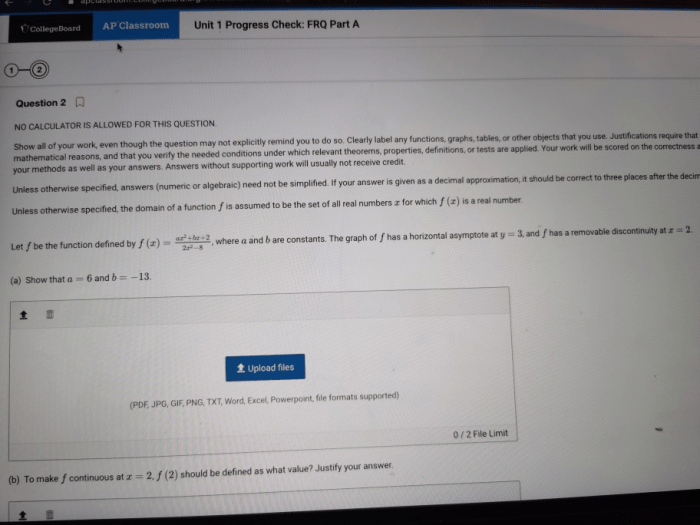
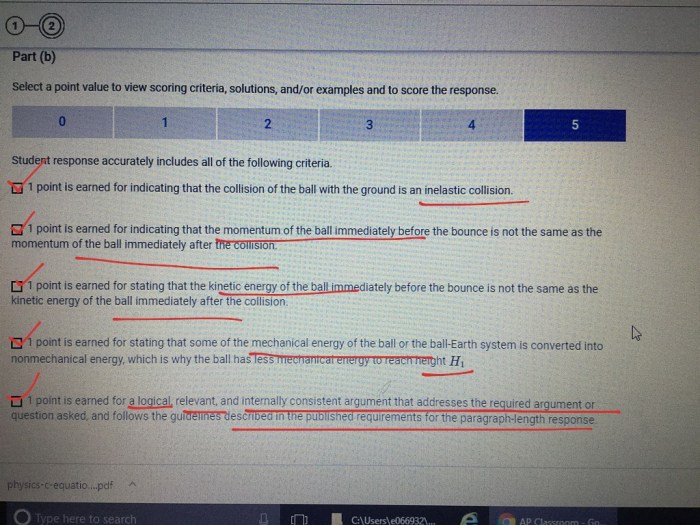
Question & Answer Hub
What are the limitations of using GDP as a measure of economic well-being?
GDP does not account for factors such as income distribution, environmental quality, or leisure time, which can contribute to overall well-being.
What are the key characteristics of different stages of economic growth?
Early stages are characterized by high population growth, low capital accumulation, and subsistence agriculture, while later stages feature low population growth, high capital accumulation, and a shift towards services.
What are the different types of unemployment?
Types of unemployment include frictional unemployment (temporary job search), structural unemployment (skill mismatch), cyclical unemployment (economic downturns), and seasonal unemployment (weather-related).
